The atomic radius of a chemical element is the distance from the center of the nucleus to the outermost shell of an electron. Since the boundary is not a well-defined physical entity, there are various non-equivalent definitions of atomic radius. Depending on the definition, the term may apply only to isolated atoms, or also to atoms in condensed matter, covalently bound in molecules, or in
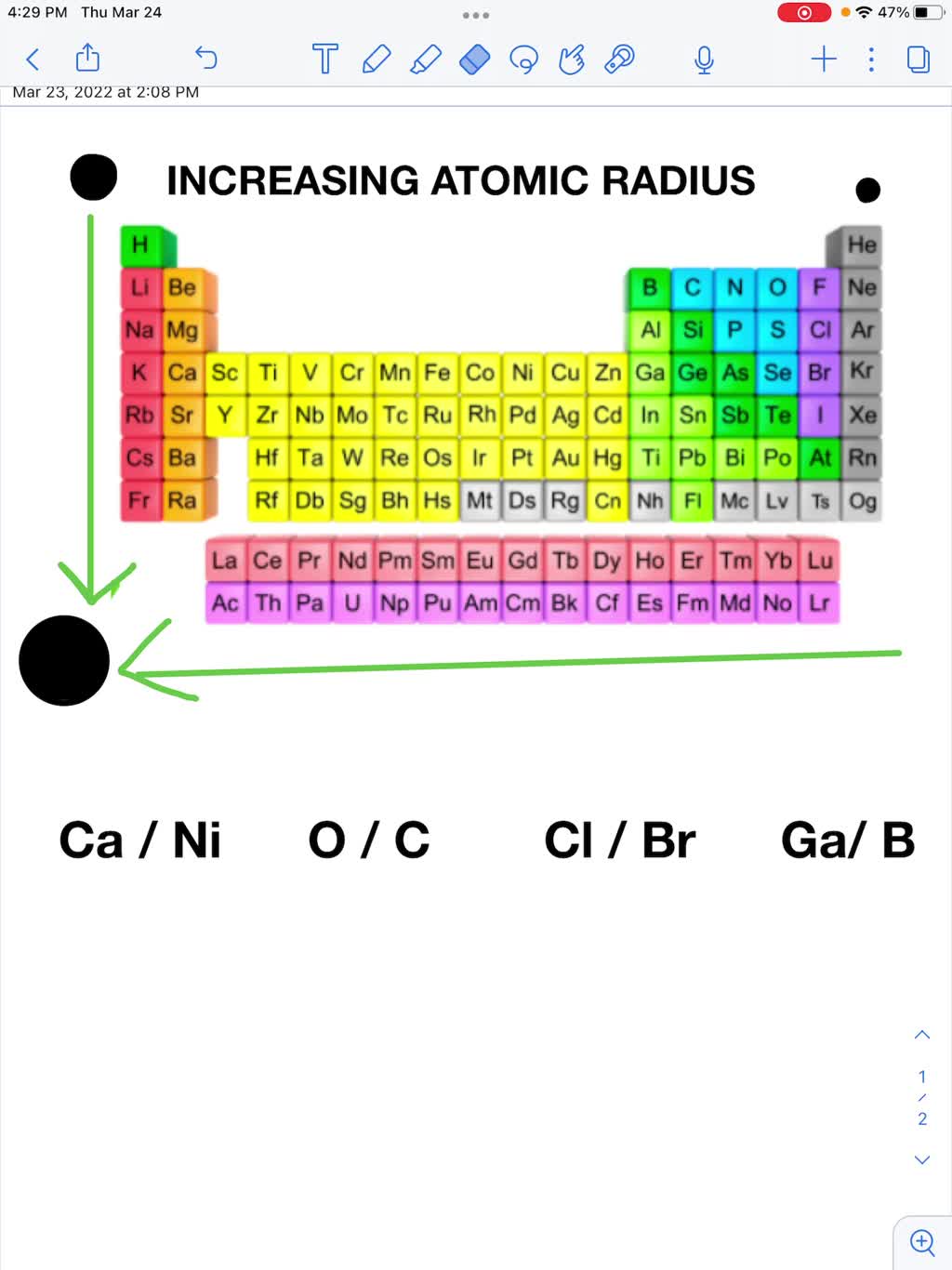
SOLVED: Use the periodic table and your knowledge of periodic trends to answer the following questions Which atom in each pair has the larger atomic radius (circle)? a) Ca or Ni Ga
The Electron Configurations: Exceptions 9m. The Electron Configuration: Ions 12m. Paramagnetism and Diamagnetism 4m. The Electron Configuration: Quantum Numbers 7m. Valence Electrons of Elements 8m. Periodic Trend: Metallic Character 3m. Periodic Trend: Atomic Radius 4m. Periodic Trend: Ionic Radius 7m. Periodic Trend: Ionization Energy 6m.

Source Image: nagwa.com
Download Image
Each atom is shown relative to the largest atom, cesium. You can download a PDF version of the table for printing. Atomic Radius Trend on the Periodic Table The size of neutral atoms is drawn from the atomic radius, which is half the distance between two atoms that are just touching each other.
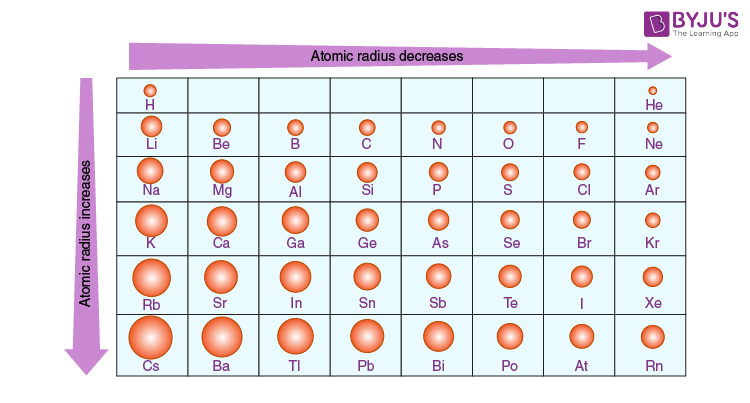
Source Image: byjus.com
Download Image
Atoms and Periodic Trends: Your MCAT Guide | BeMo®
Chemistry Chemistry questions and answers An atom of which of the following elements has the largest atomic radius? a. Po b. Cs c. At d. Pb e. Bi This problem has been solved! You’ll get a detailed solution from a subject matter expert that helps you learn core concepts. See Answer
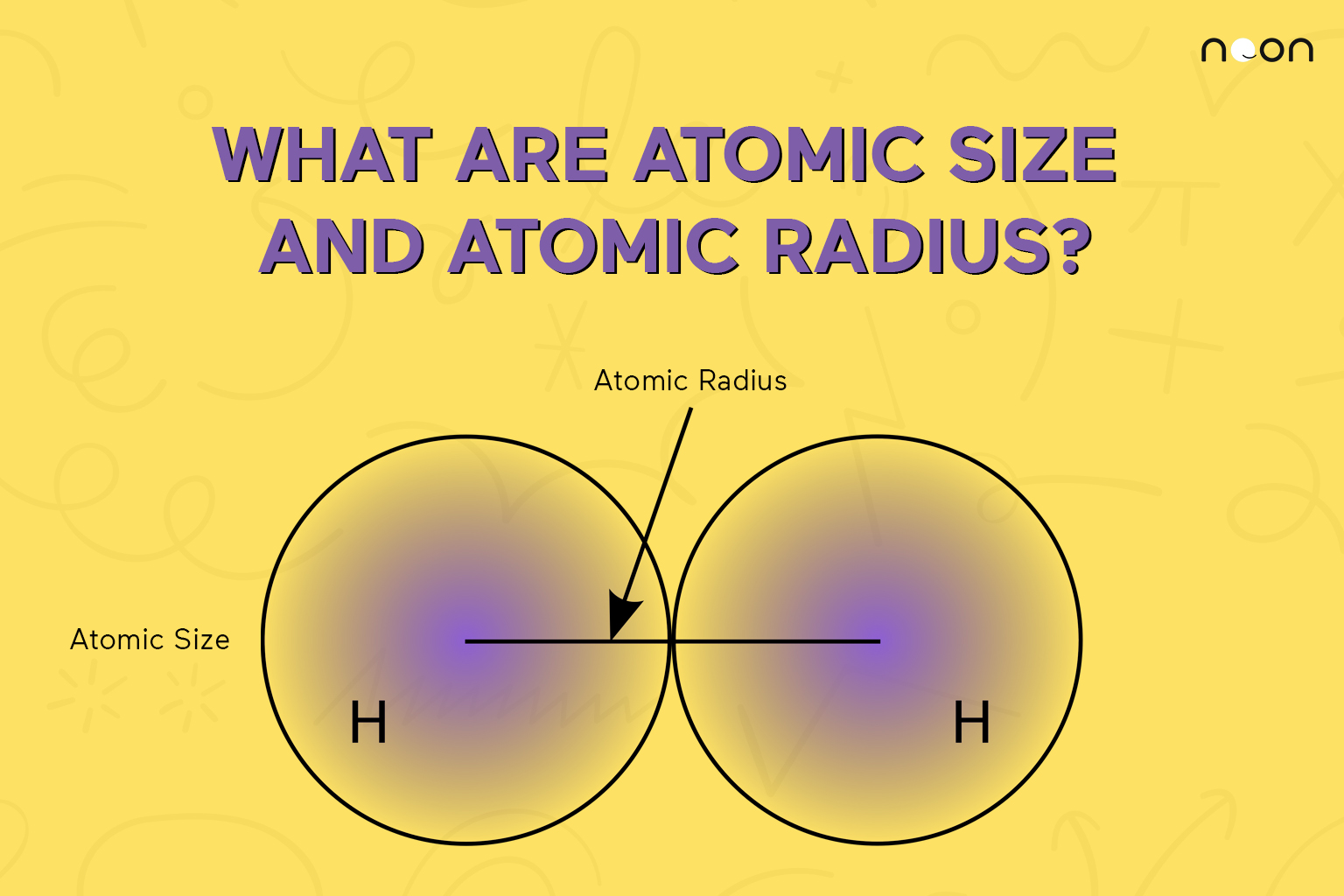
Source Image: learnatnoon.com
Download Image
An Atom Of Which Element Has The Largest Atomic Radius
Chemistry Chemistry questions and answers An atom of which of the following elements has the largest atomic radius? a. Po b. Cs c. At d. Pb e. Bi This problem has been solved! You’ll get a detailed solution from a subject matter expert that helps you learn core concepts. See Answer
9 years ago. No. Shell 1: 2 electrons. Shell 2: 8 electrons. Shell 3: 18 electrons. Shell 4: 32 electrons. Shells 5 through 7: 32 electrons in any known element, however there are additional orbitals available to hold even more electrons, but there is no element with a large enough atomic number to fill up those slots.
Atomic size and atomic radius explained | Noon Academy
Each atom’s size is relative to the largest element, cesium. Atom size values are calculated from atomic radius data. This table shows how the atom size, and atomic radius values change as you move horizontally and vertically across the periodic table. In general, atomic radius or atom size decreases as you move from left to right.
savvy-chemist: Periodicity (1) Ionisation energy and electronegativity of the elements

Source Image: derekcarrsavvy-chemist.blogspot.com
Download Image
The importance of the Periodic Table in O-level Chemistry
Each atom’s size is relative to the largest element, cesium. Atom size values are calculated from atomic radius data. This table shows how the atom size, and atomic radius values change as you move horizontally and vertically across the periodic table. In general, atomic radius or atom size decreases as you move from left to right.

Source Image: geniebook.com
Download Image
SOLVED: Use the periodic table and your knowledge of periodic trends to answer the following questions Which atom in each pair has the larger atomic radius (circle)? a) Ca or Ni Ga
The atomic radius of a chemical element is the distance from the center of the nucleus to the outermost shell of an electron. Since the boundary is not a well-defined physical entity, there are various non-equivalent definitions of atomic radius. Depending on the definition, the term may apply only to isolated atoms, or also to atoms in condensed matter, covalently bound in molecules, or in
Source Image: numerade.com
Download Image
Atoms and Periodic Trends: Your MCAT Guide | BeMo®
Each atom is shown relative to the largest atom, cesium. You can download a PDF version of the table for printing. Atomic Radius Trend on the Periodic Table The size of neutral atoms is drawn from the atomic radius, which is half the distance between two atoms that are just touching each other.

Source Image: bemoacademicconsulting.com
Download Image
Chemistry!!! Not Mystery : Periodic Property: Size of the atom/ atomic radius
An atom such as chlorine has both a covalent radius (the distance between the two atoms in a Cl2 C l 2 molecule) and a van der Waals radius (the distance between two Cl atoms in different molecules in, for example, Cl2(s) C l 2 ( s) at low temperatures). These radii are generally not the same (part (d) in Figure 2.8.2).

Source Image: chemistrynotmystery.com
Download Image
Understanding Atomic Radius Trends: The 2 Key Principles
Chemistry Chemistry questions and answers An atom of which of the following elements has the largest atomic radius? a. Po b. Cs c. At d. Pb e. Bi This problem has been solved! You’ll get a detailed solution from a subject matter expert that helps you learn core concepts. See Answer
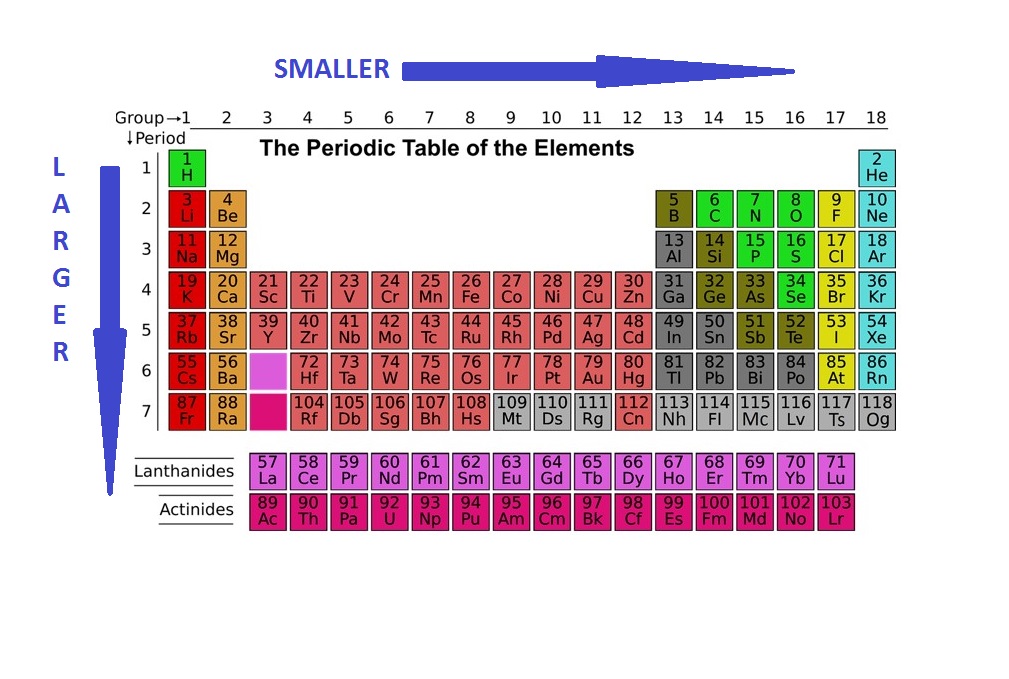
Source Image: blog.prepscholar.com
Download Image
What Is The Heaviest Element In The Universe? | IFLScience
9 years ago. No. Shell 1: 2 electrons. Shell 2: 8 electrons. Shell 3: 18 electrons. Shell 4: 32 electrons. Shells 5 through 7: 32 electrons in any known element, however there are additional orbitals available to hold even more electrons, but there is no element with a large enough atomic number to fill up those slots.

Source Image: iflscience.com
Download Image
The importance of the Periodic Table in O-level Chemistry
What Is The Heaviest Element In The Universe? | IFLScience
The Electron Configurations: Exceptions 9m. The Electron Configuration: Ions 12m. Paramagnetism and Diamagnetism 4m. The Electron Configuration: Quantum Numbers 7m. Valence Electrons of Elements 8m. Periodic Trend: Metallic Character 3m. Periodic Trend: Atomic Radius 4m. Periodic Trend: Ionic Radius 7m. Periodic Trend: Ionization Energy 6m.
Atoms and Periodic Trends: Your MCAT Guide | BeMo® Understanding Atomic Radius Trends: The 2 Key Principles
An atom such as chlorine has both a covalent radius (the distance between the two atoms in a Cl2 C l 2 molecule) and a van der Waals radius (the distance between two Cl atoms in different molecules in, for example, Cl2(s) C l 2 ( s) at low temperatures). These radii are generally not the same (part (d) in Figure 2.8.2).